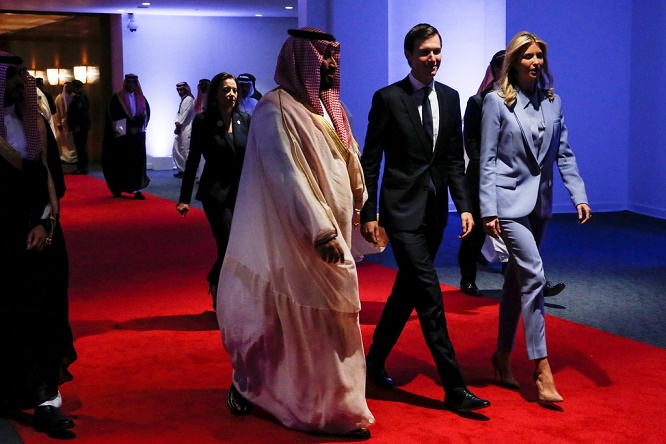
Senior American officials were worried. Since the
early months of the Trump administration, Jared
Kushner, the president’s son-in-law and Middle East
adviser, had been having private, informal
conversations with Prince Mohammed bin Salman, the
favorite son of Saudi Arabia’s king.
Given Mr. Kushner’s political inexperience, the private exchanges could make him susceptible to Saudi manipulation, said three former senior American officials. In an effort to tighten practices at the White House, a new chief of staff tried to reimpose longstanding procedures stipulating that National Security Council staff members should participate in all calls with foreign leaders.
But even with the restrictions in place, Mr. Kushner, 37, and Prince Mohammed, 33, kept chatting, according to three former White House officials and two others briefed by the Saudi royal court. In fact, they said, the two men were on a first-name basis, calling each other Jared and Mohammed in text messages and phone calls.
The exchanges continued even after the Oct. 2 killing of Jamal Khashoggi, the Saudi journalist who was ambushed and dismembered by Saudi agents, according to two former senior American officials and the two people briefed by the Saudis.
As the killing set off a firestorm around the world and American intelligence agencies concluded that it was ordered by Prince Mohammed, Mr. Kushner became the prince’s most important defender inside the White House, people familiar with its internal deliberations say.
Mr. Kushner’s support for Prince Mohammed in the moment of crisis is a striking demonstration of a singular bond that has helped draw President Trump into an embrace of Saudi Arabia as one of his most important international allies.
But the ties between Mr. Kushner and Prince Mohammed did not happen on their own. The prince and his advisers, eager to enlist American support for his hawkish policies in the region and for his own consolidation of power, cultivated the relationship with Mr. Kushner for more than two years, according to documents, emails and text messages reviewed by The New York Times.
A delegation of Saudis close to the prince visited the United States as early as the month Mr. Trump was elected, the documents show, and brought back a report identifying Mr. Kushner as a crucial focal point in the courtship of the new administration. He brought to the job scant knowledge about the region, a transactional mind-set and an intense focus on reaching a deal with the Palestinians that met Israel’s demands, the delegation noted.
Even then, before the inauguration, the Saudis were trying to position themselves as essential allies who could help the Trump administration fulfill its campaign pledges. In addition to offering to help resolve the dispute between Israel and the Palestinians, the Saudis offered hundreds of billions of dollars in deals to buy American weapons and invest in American infrastructure. Mr. Trump later announced versions of some of these items with great fanfare when he made his first foreign trip: to an Arab-Islamic summit in Riyadh, the Saudi capital. The Saudis had extended that invitation during the delegation’s November 2016 visit.
“The inner circle is predominantly deal makers who lack familiarity with political customs and deep institutions, and they support Jared Kushner,” the Saudi delegation wrote of the incoming administration in a slide presentation obtained by the Lebanese newspaper Al Akhbar, which provided it to The Times. Several Americans who spoke with the delegation confirmed the slide presentation’s accounts of the discussions.
The courtship of Mr. Kushner appears to have worked.
Only a few months after Mr. Trump moved into the White House, Mr. Kushner was inquiring about the Saudi royal succession process and whether the United States could influence it, raising fears among senior officials that he sought to help Prince Mohammed, who was not yet the crown prince, vault ahead in the line for the throne, two former senior White House officials said. American diplomats and intelligence officials feared that the Trump administration might be seen as playing favorites in the delicate internal politics of the Saudi royal family, the officials said.
(After publication, a senior White House official said in a statement: “Implications that Jared inquired about the possibility of influencing the Saudi royal succession process are false.”)
By March, Mr. Kushner helped usher Prince
Mohammed into a formal lunch with Mr. Trump in a
state dining room at the White House, capitalizing
on a last minute cancellation by Chancellor Angela
Merkel of Germany because of a snowstorm.
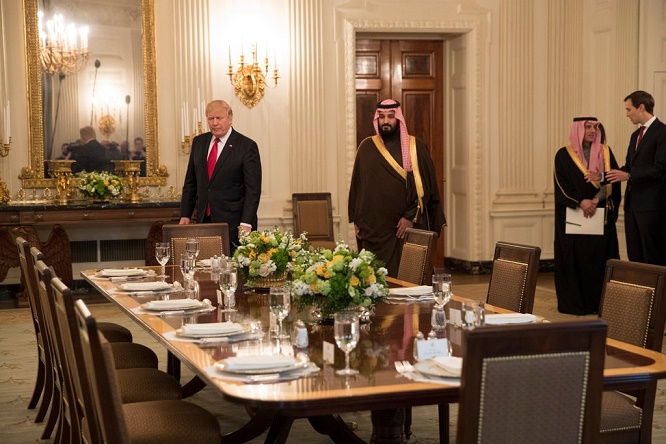

Credit: Stephen Crowley/The New York Times
Bending protocol, Mr. Kushner arranged for Prince
Mohammed, often referred to by his initials as
M.B.S., to receive the kind of treatment usually
reserved for heads of state, with photographs and
news media coverage, according to a person involved
in the arrangements. It appears to have been the
first face-to-face meeting between Mr. Kushner and
the prince, but Mr. Kushner raised eyebrows by
telling others in the White House that he and Prince
Mohammed had already spoken several times before,
two people at the event recalled.
In a statement, a White House spokesman said that “Jared has always meticulously followed protocols and guidelines regarding the relationship with MBS and all of the other foreign officials with whom he interacts.”
White House officials declined to explain those protocols and guidelines, and declined to comment on Mr. Kushner’s one-on-one communications with Prince Mohammed since the killing of Mr. Khashoggi.
Their connection, though, has been pivotal since the start of the Trump administration.
“The relationship between Jared Kushner and Mohammed bin Salman constitutes the foundation of the Trump policy not just toward Saudi Arabia but toward the region,” said Martin Indyk, a fellow at the Council on Foreign Relations and a former Middle East envoy. The administration’s reliance on the Saudis in the peace process, its support for the kingdom’s feud with Qatar, an American ally, and its backing of the Saudi-led intervention in Yemen, he said, all grew out of “that bromance.”
‘You Will Love Him’
Before the 2016 presidential race, Mr. Kushner’s most extensive exposure to the Middle East was through Israel. Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu was a Kushner family friend, and the Kushners had contributed heavily to Israeli nonprofits supporting Jewish settlements in the Palestinian territories of the West Bank.
But the Arab rulers of the oil-rich Persian Gulf mainly figured in Mr. Kushner’s life as investors in American real estate, the Kushner family business.
So Tom Barrack, a Lebanese-American real estate investor with close ties to both Mr. Trump and the Gulf rulers, set out during the campaign to introduce Mr. Kushner to his associates as a useful ally.
“You will love him and he agrees with our
agenda!” Mr. Barrack wrote in May 2016 in an email
to the Emirati ambassador in Washington, Youssef
Otaiba.
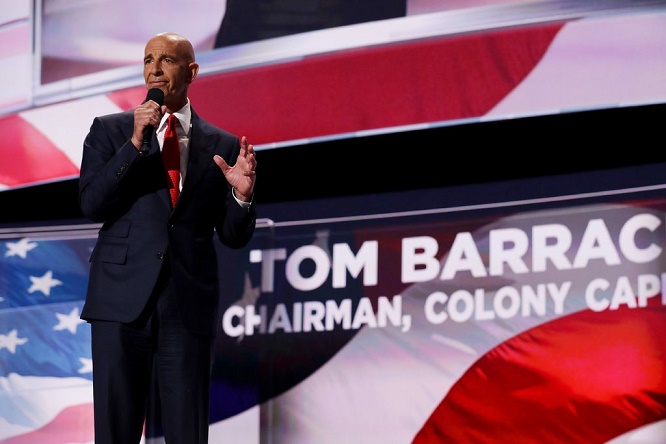

Credit: Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images
Mr. Otaiba soon positioned himself as an informal
adviser on the region to Mr. Kushner.
“Thanks to you, I am in constant contact with Jared and that has been extremely helpful,” Mr. Otaiba wrote to Mr. Barrack in the first months after Mr. Trump took office.
The Emirati ambassador was also eagerly promoting Prince Mohammed. Since the prince’s aging father had taken the throne in 2015, the Emiratis were betting heavily on the prince as their preferred contender in the succession struggles within the Saudi royal family.
“MBS is incredibly impressive,” Mr. Otaiba wrote Mr. Barrack in June 2016, as they tried to arrange meetings between the prince and the Trump campaign.
The month after the American election, the de facto ruler of the United Arab Emirates — Crown Prince Mohammed bin Zayed of Abu Dhabi — delivered a similar message when he made an unannounced trip to New York for a meeting with Mr. Kushner and others about the Israeli-Palestinian peace process.
While speaking with Mr. Kushner, the Emirati prince also recommended Prince Mohammed of Saudi Arabia as a promising young leader, according to a person familiar with their conversations.
Mr. Kushner seemed impressed. The meeting had been arranged in part by Rick Gerson, a hedge fund manager who was close to Mr. Kushner and to the Emirati crown prince. After the encounter, Mr. Gerson sent a message to the Emirati crown prince about his success in winning over Mr. Kushner.
“I promise you this will be the start of a special and historic relationship,” Mr. Gerson wrote, in a text message.
On the eve of the inauguration, Mr. Gerson wrote to the Emirati crown prince again.
“You have a true friend in the White House,” Mr. Gerson wrote, recounting a visit with Mr. Kushner before Mr. Kushner departed for Washington.
The emails with Ambassador Otaiba and the text messages with Mr. Gerson were provided to The Times by people critical of Emirati foreign policies and authenticated by others with direct knowledge of their contents. Mr. Gerson declined to comment and the Emirati embassy did not respond to requests for comment.
‘Lack of Familiarity’ With History
Top aides to Saudi Arabia’s Prince Mohammed also met with Mr. Kushner on a trip to New York in November 2016, after the election.
The Saudi team included Musaad al-Aiban, a cabinet minister involved in economic planning and national security, and Khaled al-Falih, installed by the prince as minister of energy and chairman of the state oil company, according to executives who met with them and a person who was briefed on the meetings. Mr. Aiban did not respond to a request for comment, and Mr. Falih could not be reached for comment.
The delegation made special note of what it
characterized as Mr. Kushner’s ignorance of Saudi
Arabia.

2016.
Credit: Tasneem Alsultan for The New York Times
“Kushner made clear his lack of familiarity with the
history of Saudi-American relations and he asked
about its support for terrorism,” the team noted in
the slide presentation prepared for Riyadh. “After
the discussion, he expressed his satisfaction with
what was explained about the Saudi role in fighting
terrorism” and what the Saudis said was their
international leadership in fighting Islamist
extremism.
Mr. Kushner, the Saudi report said, also questioned the delegation’s motives, asking whether the group had always been interested in working with Mr. Trump. As a candidate, Mr. Trump had promised to ban Muslim immigrants from entering the United States and had singled out Saudi Arabia as a dangerous influence.
“Kushner wondered about Saudi Arabia’s desire for partnership and whether it came from opportunity or worry, and he wondered as well if it was specific to this American administration or whether it was presented to Hillary Clinton (for example: women driving),” read another slide, next to a photograph of Mr. Kushner.
But Mr. Kushner was clear about his own priorities, the report said. “The Israeli-Palestinian conflict was among the most important issues to draw Kushner’s attention,” the delegation reported, and therefore the best way to win him over.
“The Palestinian issue first: there is still no clear plan for the American administration toward the Middle East,” the delegation wrote, “except that the central interest is finding a historic solution to support the stability of Israel and solve the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.”
To cultivate ties with the Trump team, the Saudis had prepared a long list of initiatives that they said would help Mr. Trump deliver for his supporters.
Seizing on Mr. Trump’s campaign vows for the “extreme vetting” of immigrants, the Saudi delegation proposed “establishing an intelligence and data” exchange “to help the American administration carry out its strategy of investigating those requesting residency (extreme vetting),” according to an Arabic version of a presentation for the Trump team.
And the delegation pledged “high-level coordination with the new American administration” to help with “defeating extremist thought.”
Several of the Saudi proposals were evidently welcomed.
One was a “joint center to fight the ideology of extremism and terrorism.” President Trump helped inaugurate a Saudi version of the center on his trip to Riyadh the following May.
Another Saudi proposal outlined what the Trump administration later called “an Arab NATO.” In their presentation, the Saudis described it as an Islamic military coalition of tens of thousands of troops “ready when the president-elect wishes to deploy them.”
Other initiatives appeared timed to Mr. Trump’s first term in office, like proposals to spend $50 billion over four years on American defense contracts, to increase Saudi investment in the United States to $200 billion over four years, and to invest, with other Gulf states, up to $100 billion in American infrastructure.
And the delegation urged Mr. Trump to come to Saudi Arabia himself to “launch the initiatives as part of a historic welcome celebration.”
It is unclear how the delegation’s slide-show presentation to and about the Trump team were obtained by the Al Akhbar newspaper, which is sympathetic to the Iranian-backed Lebanese movement Hezbollah and Iran, an enemy of Saudi Arabia.
Several Americans identified in the presentation acknowledged meeting with the delegation and confirmed broad outlines of the discussions. The Times provided the documents and the names of delegation members to an official of the Saudi Embassy in Washington, who declined to comment.
A Saudi Role in Mideast Peace
Israel had long argued to American diplomats that Saudi Arabia’s influence in the region made it essential to any peace deal, and the Israelis were developing high hopes for Prince Mohammed because of his hawkish views toward Iran and his general iconoclasm (he would later make several statements, like affirming the Israeli “right” to land, that were notably more sympathetic to the Israeli position than those of other Saudi leaders.)
Within weeks of Mr. Trump’s move into the White House, Mr. Kushner had embraced the delegation’s proposal for the president to visit Riyadh, convinced by then that the alliance with Saudi Arabia would be crucial in his plans for the region, according to a person who discussed it with Mr. Kushner and a second person familiar with his plans.
The secretary of state at the time, Rex W.
Tillerson, opposed the idea. It would link the
administration too closely to Riyadh, these people
said, giving up flexibility and leverage. Mr. Trump
initially saw little benefit either, according to a
person involved in his deliberations.

visit last year.
Credit: Stephen Crowley/The New York Times
But by the time of the inauguration Mr. Kushner was
already arguing that under the influence of Prince
Mohammed, Saudi Arabia could play a pivotal role in
advancing a Middle East peace deal, according to
three people familiar with his thinking. That would
be the president’s legacy, Mr. Kushner argued,
according to a person involved in the discussions.
It was around the time of the White House visit in March 2017 that senior officials in the State Department and the Pentagon began to worry about the one-on-one communications between Prince Mohammed — who is known to favor the online messaging service WhatsApp — and Mr. Kushner. “There was a risk the Saudis were playing him,” one former White House official said, speaking on condition of anonymity to discuss internal deliberations.
Two later face-to-face encounters with Mr. Kushner preceded key turning points in Prince Mohammed’s consolidation of power.
Shortly after Mr. Kushner visited Riyadh with the president in May 2017, Prince Mohammed orchestrated the ouster of his older cousin, Prince Mohammed bin Nayef, removing him from control of the Saudi Interior Ministry and replacing him as crown prince. Prince Mohammed also announced a Saudi-led blockade of its neighbor and rival Qatar, the host of a major American air base.
And days after Mr. Kushner made an unannounced visit to Riyadh in the fall of 2017, the crown prince summarily detained about 200 wealthy Saudis, including several of his royal cousins, in a Ritz-Carlton hotel in Riyadh.
After each play for power, President Trump
publicly praised Prince Mohammed.
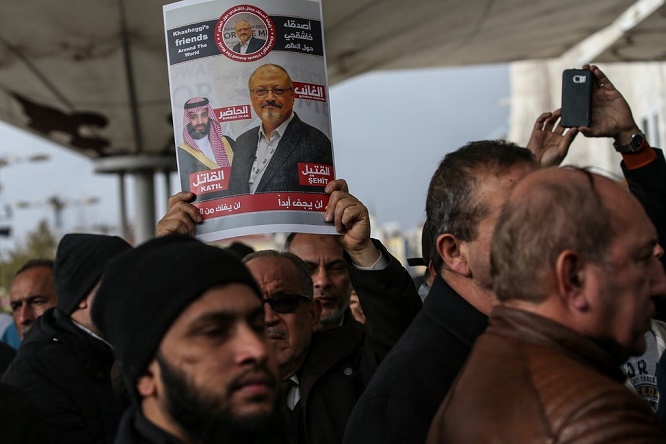

Credit: Emrah Gurel/Associated Press
One former White House official argued that Mr.
Kushner’s personal ties to Prince Mohammed had
sometimes been an asset. At one point, for example,
the Saudi-led coalition fighting in Yemen had
blocked a critical port, cutting off humanitarian
and medical supplies. The national security adviser
at the time, Lt. Gen. H.R. McMaster, suggested that
Mr. Kushner call Prince Mohammed to address the
issue, the official said, and General McMaster
believed Mr. Kushner’s intercession had helped
persuade the Saudis to loosen the restrictions.
White House officials also say that Mr. Kushner has formal conversations with many other leaders in the region. And previous administrations have also had close ties to the Saudi government.
Since the uproar over Mr. Khashoggi’s killing, the Trump administration has acknowledged only one conversation between Mr. Kushner and Prince Mohammed: an Oct. 10 telephone call joined by John R. Bolton, the national security adviser. The Americans “asked for more details and for the Saudi government to be transparent in the investigation process,” the White House said in a statement.
But American officials and a Saudi briefed on their conversations said that Mr. Kushner and Prince Mohammed have continued to chat informally. According to the Saudi, Mr. Kushner has offered the crown prince advice about how to weather the storm, urging him to resolve his conflicts around the region and avoid further embarrassments.
Few of the Saudi promises have amounted to much. The effectiveness of the counterterrorism center in Riyadh remains doubtful. After offering $50 billion in new weapons contracts, the Saudis have signed only letters of interest or intent without any firm deals. After proposing to marshal up to $100 billion in investments in American infrastructure, the Saudis have announced an investment of only $20 billion.
Inside the White House, Mr. Kushner has continued to argue that the president needs to stand by Prince Mohammed because he remains essential to the administration’s broader Middle East strategy, according to people familiar with the deliberations.
Whether Prince Mohammed can fulfill that role, however, remains to be seen. His initial approaches to the Palestinians were rejected by their leaders, and their resistance stiffened after the Trump administration recognized Jerusalem as Israel’s capital without waiting for a negotiated agreement on the city’s status.
Now the prince’s father, King Salman, 82, who is still the official head of state, has appeared to resist Mr. Kushner’s Middle East peace plans as well.
“The Palestinian issue will remain our primary issue,” the king declared in a speech last month, “until the Palestinian people receive all of their legal rights.”